In this series for ESG Clarity Asia, Morningstar dives into ESG funds available in Asia, analysing their investments, performance and ESG credentials.
For this latest article, Morningstar’s Samuel Lo takes a look at the Abrdn Japanese Sustainable Equity Fund.
Abrdn Japanese Sustainable Equity follows a quality-focused investment approach that has been time-tested and consistently executed over the years. The strategy’s Luxembourg-domiciled vehicle was classified as being Article 8-compliant under the EU SFDR regulations in April 2022 and added ‘sustainability’ to its name.
Kwok Chern-Yeh, head of Japan equities and deputy head of Asia Pacific equities at abrdn, has helmed this strategy since 2011. He has 18 years of investment experience and joined the firm in 2005. He leads this strategy’s three-member portfolio construction pod, a structure created in 2019 that is directly responsible for the management of the strategy. Together, they are part of the six-member Japan equity desk based in Tokyo. Chern-Yeh has consistently demonstrated impressive investment acumen over the years, although turnover within this compact team has been elevated in recent years.
The team places a strong emphasis on business quality. To determine this, the team focuses on a company’s management team and track record, its business model and competitive advantages, and the strength of the financials. Thanks to this strong focus on quality, the portfolio has a consistently higher return-on-equity and lower debt-to-equity compared with its benchmark, the MSCI Japan Index, and its peers. The portfolio is conviction-driven and concentrated, with 30-60 holdings.
Along with its conversion to SFDR Article 8 status, the fund added two portfolio-level ESG targets. The portfolio’s carbon intensity should be at least 10% lower its benchmark and its ESG rating, as measured by the MSCI ESG rating, should be better than or equal to the index. It also excludes around 20% of the investment universe via a combination of negative screening criteria, such as companies that violate the UN Global Compact or are involved in tobacco, gambling and thermal coal, as well as positive screening based on in-house ESG scoring. Given the existing high-quality focus of this strategy, there is limited impact on the strategy’s opportunity set. The portfolio currently has an average MSCI ESG rating of A, slightly ahead of its benchmark.
A key component of the team’s ESG analysis is the in-house ESG quality rating, which classifies each company on a five-tier scale ranging from best-in-class to laggards. Around a third of the portfolio is in the top two tiers, which are companies with strong ESG considerations and disclosure, while the rest are in the middle tier.
The team is also committed to active ownership of portfolio holdings. Recent engagement examples include Shin-Etsu Chemical, a major producer of the PVC material. While PVC production is carbon-intensive, the company has been trying to reduce carbon intensity by relying more on natural gas or other renewable energy as a source of electricity, and the abrdn team has encouraged the company to consider setting science-based targets.
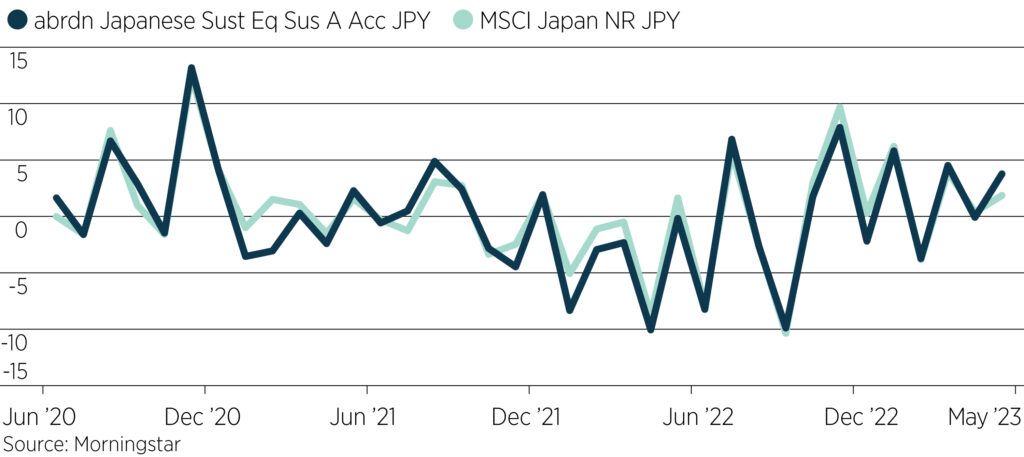
Fund performance versus index